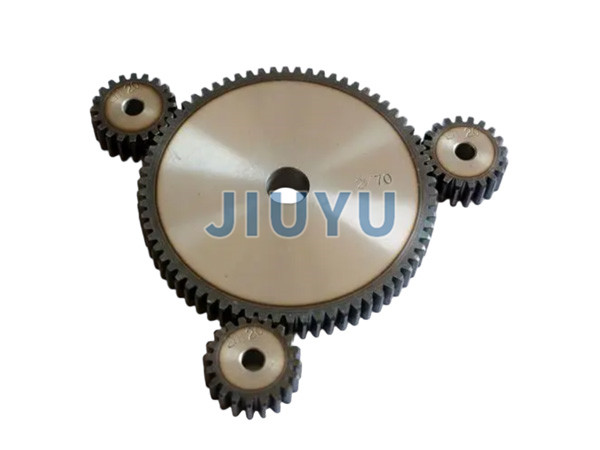
Gears are an important component widely used in mechanical transmission. Here is an introduction to their related knowledge:
Definition and Function
A gear is a mechanical component composed of teeth, hub, spokes, and other parts. Through the meshing teeth, it can achieve functions such as transmitting motion and power, changing the size and direction of speed and torque.
Classification
Classified by gear shape: there are cylindrical gears, including spur cylindrical gears, helical cylindrical gears, herringbone cylindrical gears, etc., commonly used for transmission between parallel shafts;
; Conical gears, such as spur bevel gears and helical bevel gears, are mainly used for transmission between intersecting axes; Worm gear, used for transmission between staggered shafts According to tooth surface hardness classification: it can be divided into soft tooth surface gears (tooth surface hardness ≤ 350HBS), which have simple manufacturing processes, low costs, and are commonly used in situations where precision and load-bearing capacity are not high requirements; Hard tooth surface gears (tooth surface hardness>350HBS), after quenching, carburizing and other heat treatments, have good tooth surface hardness and load-bearing capacity, suitable for high-speed and heavy-duty transmission applicationsDesign Parameters
Modulus: It is an important parameter for measuring the size of gears. The larger the modulus, the larger the teeth, and the greater the load that the gear can withstand.
. It is equal to the ratio of the diameter of the gear indexing circle to the number of teeth Number of teeth: It directly affects the transmission ratio and speed of gears. In the transmission system, different gear combinations with different numbers of teeth can achieve different transmission ratio requirements Pressure angle: usually refers to the pressure angle on the dividing circle, and the standard pressure angle specified in Chinese standards is 20 °. The pressure angle affects the shape and force distribution of the gear teeth. The larger the pressure angle, the thicker and stronger the tooth root, but the transmission efficiency may slightly decreaseMaterial Selection
Common gear materials include medium carbon steel (such as 45 steel), medium carbon alloy steel (such as 40Cr, 20CrMnTi, etc.), cast steel, and some non-metallic materials (such as engineering plastics).
. For gears that can withstand heavy loads and impacts, medium carbon alloy steel is generally selected, and good comprehensive mechanical properties can be obtained after heat treatment; For light load and low-speed gears, medium carbon steel or cast steel can be used; In some situations where high noise requirements and low loads are needed, non-metallic materials can be used to make gearsApplication Industry
Automotive Industry: Used for components such as transmissions and differentials to achieve variable speed and power distribution in automobiles, enabling them to maintain appropriate speed and power under different driving conditions.
Machine tool industry: In the transmission system of machine tools, different combinations of gears are used to achieve different speeds and feed motions of components such as worktable and spindle, protecting machining accuracy and efficiency Aerospace industry: Applied to aircraft engine transmission systems, landing gear retraction mechanisms, etc., gears are required to have high strength, lightweight, and reliable performance to meet the special working requirements of aerospace equipment Industrial robots: used for joint transmission of robots, enabling each joint of the robot to achieve accurate motion and positioning, protecting the accuracy and stability of the robot's movements